| Project Name | Technologies | Affiliation | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Novelty Oriented AI Agent - DARPA SAIL-ON Project | Symbolic Reasoning & Planning, RL, Java | AIR Lab + HRI Lab @ Tufts | Jan 2020 - May 2020 |
| Visualizing a Robot's Perspective in Augmented Reality | ROS, Unity, C++, C#, Python | AIR Lab @ Tufts | May 2018 - May 2019 |
| Robot Teleoperation through Neuromuscular Control | Go, Vincross Hexa, Docker | CTRL Labs | May 2019 |
| Trinity College International Fire Fighting Robot Contest | ROS, C++, Python, Raspberry Pi, Arduino | Tufts Robotics Club | Sep 2018 - April 2019 |
| Sound Based Robot Localization | MATLAB, Machine Learning | Probabilistic Robotics Class | May 2019 |
| Clappy Bird | VHDL, FPGA, Lattice Radiant | Digital Circuits Class | May 2019 |
| Programming Robots through Paper Worksheets | OpenCV, C++, LabVIEW | Center for Engineering Education and Outreach | June 2017 - August 2017 |
Novelty Oriented AI Agent - DARPA SAIL-ON Project
AIR Lab + HRI Lab @ Tufts, Jan 2020 - May 2020
Technologies Used: Symbolic Reasoning & Planning, RL, Java
Motivation:
- The SAIL-ON program was created by DARPA
- Develop AI that can recognize, handle and adapt to novel environmental changes
- Shift focus beyond limited and controlled domains to more “open-world” ones
- Polycraft (a Minecraft mod) was chosen as one of such environments
Role:
- Designed and developed software pipelines to parse sensory information, execute actions, generate facts, plan and learn
- Pioneered the Novelty Detection capabilities of the agent to not only recognize environmental changes but also express them symbolically
- Led a group of graduate and undergraduate students to publish the system architecture
Technical Details:
- The cognitive architecture aims to integrate symbolic approaches (Planning, Logical Reasoning etc.) and neural approaches (Reinforcement Learning, Deep Learning etc.)
- Specifics to be published soon
Results:
- Agent achieved top performance in independent external evaluations against other approaches
- Paper regarding the agent architecture has been accepted to AAMAS 2021
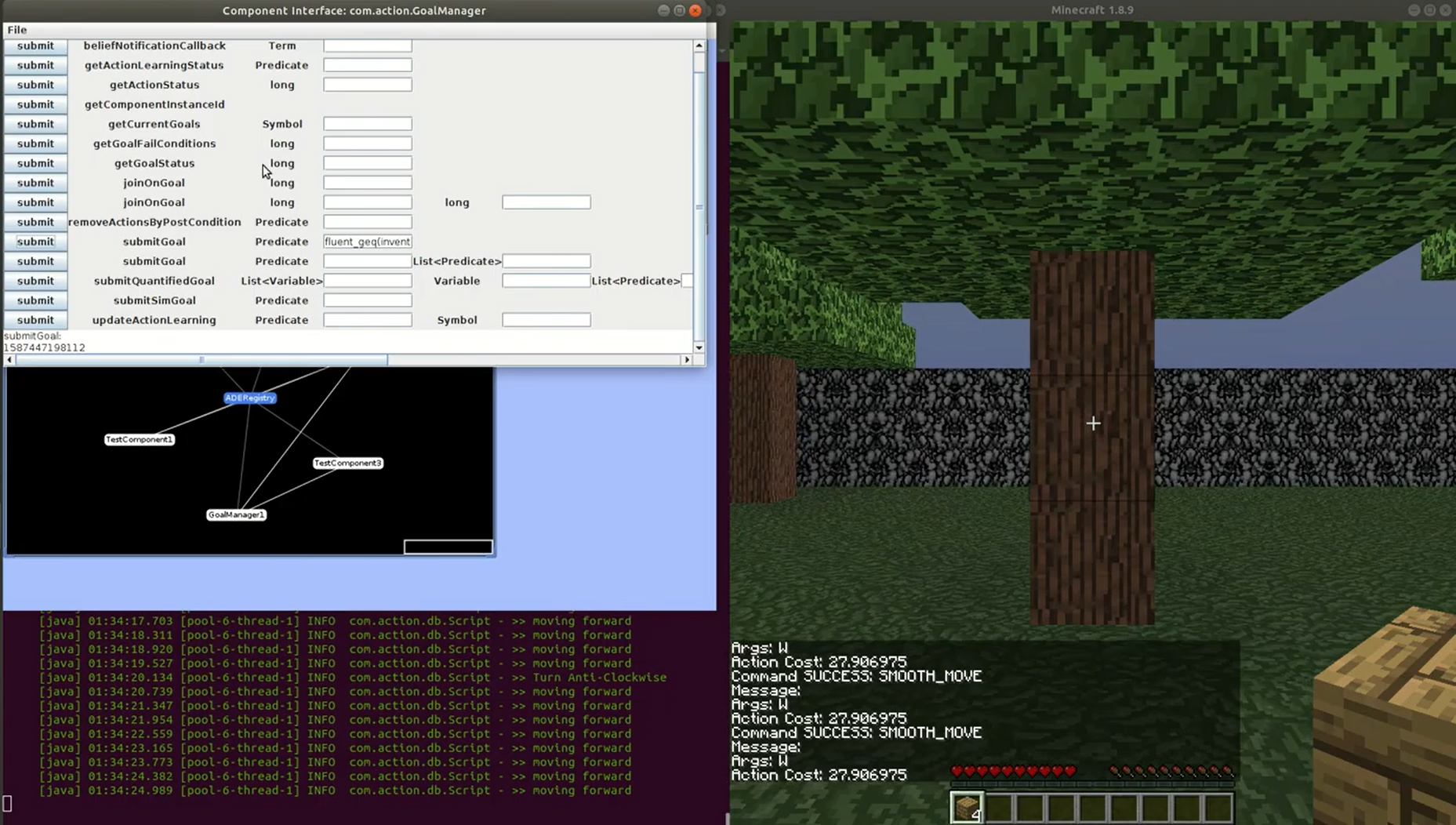
Visualizing a Robot’s Perspective in Augmented Reality
AIR Lab @ Tufts, May 2018 - May 2019
Technologies Used: ROS, Unity, C++, C#, Python
Motivation:
- Internal state of robots is often highly esoteric
- Develop a fast, high-bandwidth and accessible medium to convey it
- Valuable for human-robot interaction and robotics education
Role:
- Proposed the project for Tufts Summer Scholars and received funding to pursue it
- Designed the overall system architecture and the information pipeline
- Developed ROS Nodes in C++ to transform, sample and compress robot data
- Developed a Unity application to request and parse the data into visualizations
- Developed the visual tracking system using Vuforia SDK and Laser Cutting
Technical Details:
- Supports visualizations of robot perception, belief and planning
- Specific types include LIDAR, Costmap, Path Planning, Localization Particles
- Supports Hololens, iPad, Android phones and tablets
Results:
- Presented a Late Breaking Report in HRI 2019 conference in South Korea
- Part of the Tufts entry that won Verizon 5G EdTech Challenge and the $100K prize
- Featured in an official Tufts University video and an article
- Video below shows a screen-recording as captured from an iPad
Robot Teleoperation through Neuromuscular Control
CTRL Labs, May 2019
Technologies Used: Go, Vincross Hexa, Docker
Motivation:
- Humans have evolved to have a very fine control over our wrist and hands
- Interfaces that can extend this degree of control to robots can be valuable
- Remote teleoperation, learning by demonstration and semi-autonomous operation
Role:
- Mapped EMG-based readings of muscle activations to hexapod’s appendages
- Developed capability to mimic finger movements of a human hand
- Developed capabiltity to kick individual legs and navigate for soccer
- Helped filming of the demo to NPR for their CTRL Labs documentary
Technical Details:
- Developed an API in Go programming language for CTRL Kit
- Developed logic to parse neuromuscular information into motor commands
- Generated action requests for the robot’s body parts concurrently
Results:
- The NPR video below introduces the technology and shows the hexapod in action
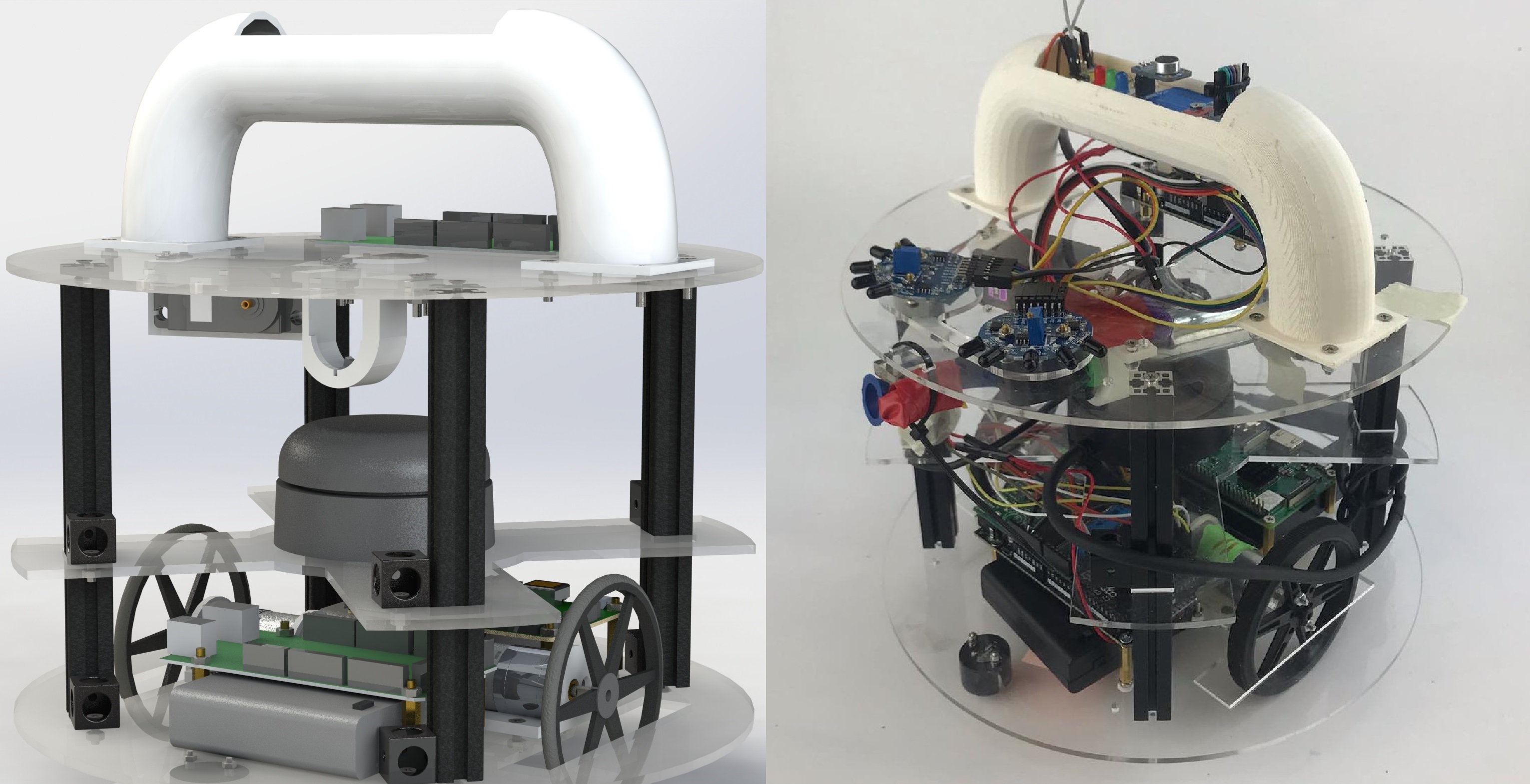
Trinity College International Fire Fighting Robot Contest
Tufts Robotics Club, Sep 2018 - April 2019
Technologies Used: ROS, C++, Python, Raspberry Pi, Arduino
Motivation:
- Yearly contest held in Trinity College that simulates a fire-emergency scenario
- Develop a robot design that can be iteratively improved upon in subsequent years
Role:
- Led the development of the club’s first ROS-enabled robot in 2019
- Managed hardware, electrical and software teams
- Taught ROS to fellow members
Technical Details:
- A central Raspberry Pi 3B+ running ROS
- An Arduino Mega interacting with sensors and actuators in real time
- Equipped with LIDAR and a servo controlled fire-extinguisher
- Biggest challenges:
- Limited computation power of the Pi
- Tuning the mapping and path-planning algorithms
- Developing a robust navigation stack
Results:
- Capable of point-point navigation in an unknown environment using SLAM
- Club’s first functional ROS-powered robot
- Won the Olympiad in Senior Individual Category in 2018 and 2019
Sound Based Robot Localization
Probabilistic Robotics Class, May 2019
Technologies Used: MATLAB, Machine Learning
Motivation:
- Indoor navigation for robots in changing physical spaces is difficult
- Most common sensors rely on these physical features (LIDARs, Cameras)
- Acoustic properties of a room are dependent mostly on the shape of the room
- Identifying rooms based on their acoustic properties could be helpful
Role:
- Designed the proposal for the class project
- Developed software in MATLAB alongside a teammate
- Evaluated and presented our results
Technical Details:
- Used a Sine Sweep to generate Room Impulse Response (RIR)
- Extracted features from the RIR
- Used SVM on these features to predict the room
Results:
- The code, datasets and the project report can be found here
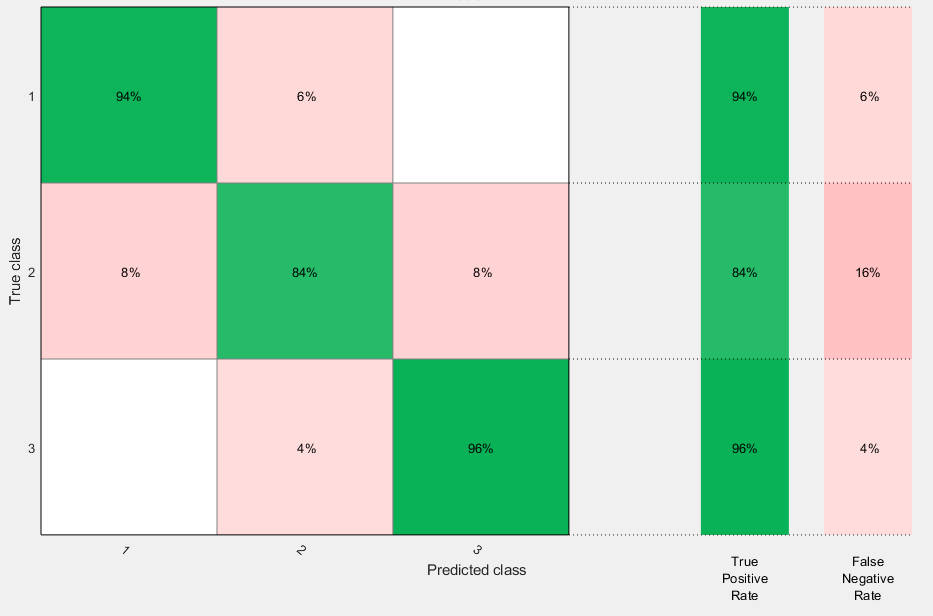
- Dataset was collected across 3 spaces with 50 samples each
- Confusion matrix below outlines our final cross-validation results
- Class 1 is a small lab room
- Class 2 is an open lounge space
- Class 3 is a section of a corridor
- Works practically perfectly between the lab room and the corridor
- Some error in the open lounge space possibly because it lacked a consistent profile
- Predicting position in the room given room information did not yield solid results
Clappy Bird
Digital Circuits Class, May 2019
Technologies Used: VHDL, FPGA, Lattice Radiant
Motivation:
- Create an interactive experience for an exposition at the end of class
Role:
- Developed digital circuits in VHDL and Lattice Radiant
- Wrote Arduino Code to parse microphone signal
Technical Details:
- Recreated the popular game Flappy Bird in an FPGA using claps as the means to control the game (hence the name)
- Used an Arduino Nano to interface with the microphone and detect claps
- Entire game logic and rendering is done within the FPGA using clocks, flip-flops, latches, multiplexers etc. in VHDL
Results:
- The code and the project report can be found here
- The video below demonstrates the system in action:
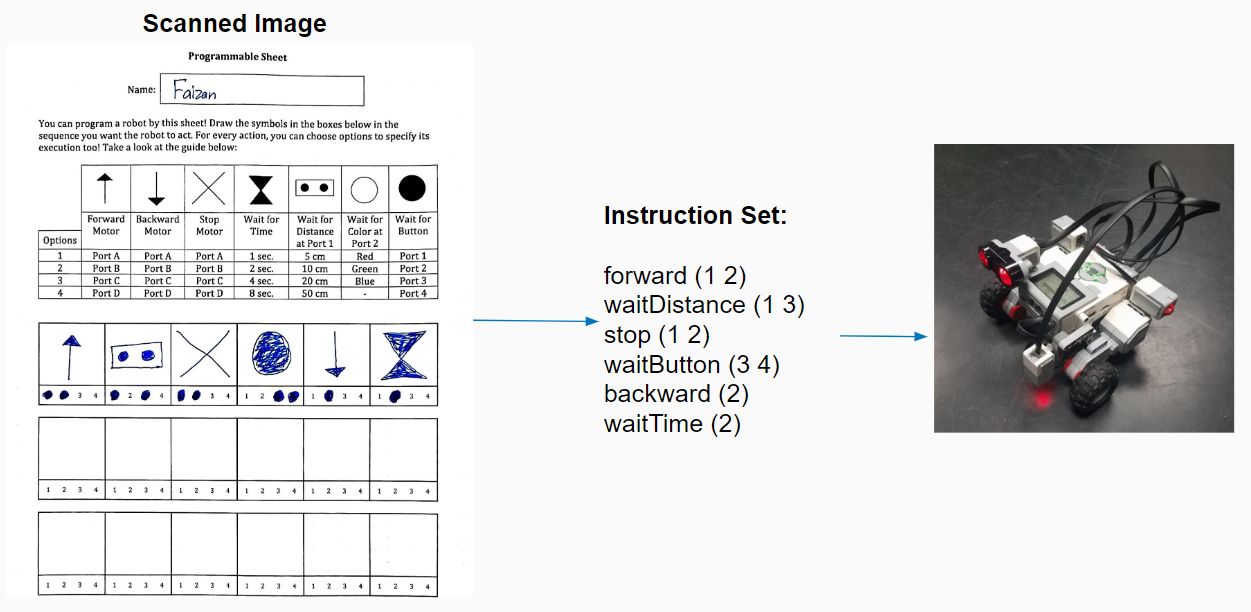
Programming Robots through Paper Worksheets
Center for Engineering Education and Outreach, June 2017 - August 2017
Technologies Used: OpenCV, C++, LabVIEW
Motivation:
- Center aims to develop technologies that enhance engineering learning
- InterLACE is a digital tool to help teachers digitize classroom workflow
- Extend InterLACE to automatically extract and organize worksheet subsections
Role:
- Developed software in C++ using Visual Studio
Technical Details:
- Devised a worksheet template format to specify subsections
- Used OpenCV to detect the sections in a scanned image using the template
- Made the subsection information available for further processing
Results:
- Implemented a programmable worksheet as a demonstration
- Young students could simply draw on the worksheet to program a LEGO robot